Your Blockchain Address
In the early days of Bitcoin, did you know that before you had your unique, long blockchain address, that you could previously send payments to an IP-address? Before the days of managing a public key and address, using IP addresses to send payment was pretty convenient, known as the “Pay to IP” methodology.
But then the Bitcoin developers were reminded of the cybersecurity threats that would soon follow, making this method of sending coins vulnerable to third-party intermediary attacks. Upon this realization, the option to send payments to an IP-address.
The purpose behind a blockchain address is simply to serve as a secure identifier for transactions--specifically, sending payments to an entity that has unique information.
New Standard for Bitcoin Addresses
After the Pay to IP mechanism was left behind, the “Pay to Public Key Hash”, or P2PKH, became the new standard format for sending payments to bitcoin addresses.
To the plain eye, it looks like this:
1K31KZXjcochXpRhjH9g5MxFFTHPi2zEXb
When you are sending payments to another P2PKH address, make sure it has 34 characters and begins with a “1”.
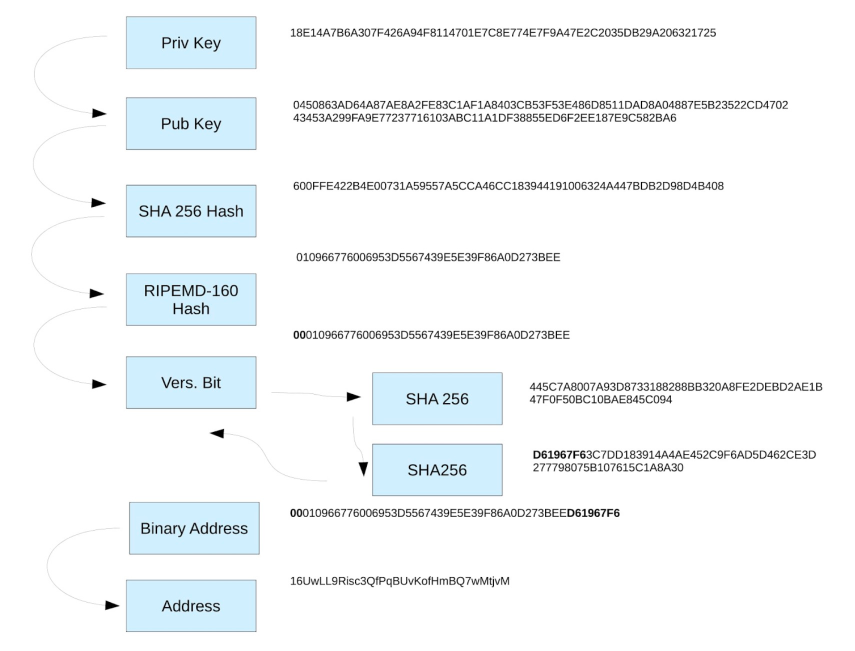
How To Get a Bitcoin (or other Blockchain Address)
For beginners, it’s very easy to create your own P2PKH address. All it requires is choosing a particular “wallet” (or software).
Once you have a wallet, the back-end (nothing you need to do) automatically collects entropy and uses it to generate an ECDSA private key. “ECDSA” is the cryptographic algorithm in the core of bitcoin addresses.
The wallet essentially pushes the public key through a series of cryptographic algorithms, eventually converting all the bytes and code into the final product: the bitcoin address.
The purpose of the asymmetric signature platform allows you to sign messages with the PRIVATE key (rather than the “public” key) and verify the signature with the Public key.
This solidifies your ownership over the address, as it’s very similar to you physically signing a letter or document.
The Public Key
Once the private key with entropy is created, the wallet generates the public key from that information by picking random coordinates on a certain elliptic curve and doing some calculations.
For your benefit, all you need to worry about is the public key, which allows you to send and receive payments.
‘65’ Too Long
However, the length of characters which comprise the public key were very long and inconvenient, running at 65 characters long. The potential for an individual to type it out wrong was enough of a reason for the bitcoin developers to create a method for deriving an address from the public key.
Are You Using the Right Key?
For beginners or even those conducting regular transactions, whenever you paste a blockchain address in your bitcoin wallet, it immediately checks the prefix and calculates the “checksum”.
A checksum address is a quick way to verify if a number, or set of data, has been altered, either intentionally or unintentionally. This prevents you from accidentally sending your crypto to a non-existent address. In other words, it solves the “clerical” or typographical error.
The checksum address is created by running the algorithm on a piece of data, generating a checksum number, or hash, which can then be sent along with the original set of data. The data recipient can then use the hash to determine whether the data has been altered or corrupted. A safeguard. If the checksum doesn’t match, it rejects the address, making it impossible to (inadvertently) send funds to a wrong address due to a clerical or typographical error.
If however, you have the private key for an address, only you can sign a transaction with the cryptocurrency token assigned to that address. In turn, everyone who knows your address can verify the validity of your signature.
In plain, all that’s happening is signing a transaction and verifying the transaction, using public and private keys.
Bitcoin’s Advanced Addresses
Source: Blockgeeks
Seeing that Bitcoin is the premiere cryptocurrency, it is fair to assume it’s a bit more advanced and sophisticated, which is why it has more advanced addresses, known as the P2SH addresses, or “Pay to Script Hash”.
P2SH addresses means the individual doesn’t pay to the hash of a public key, but rather to the hash of a script. In layman’s terms, all this means is that when signing a transaction, you don’t have to provide the signature matching a certain public key--instead a script matching a certain hash.
The purpose of this is simply to allow for more feasible and flexible means to verify yourself.
P2SH addresses use the prefix 05, beginning with a “3”. For more information on P2SH addresses, please click here.
What Do Other Cryptocurrencies Use?
It’s worth mentioning that many other cryptocurrencies, like Litecoin (LTC), Dash, and Dogecoin use a very similar address format as bitcoin.
Others, like Monero, use the Cryptonote algorithm, which deploys another cryptographic signature algorithm to generate the public key, EdDSA. These are known as Cryptonote currencies, which have “ring-signatures”, requiring the addresses to have two public keys--a view and spend key.
Similar to bitcoin addresses, Cryptonote adds a prefix byte and hashes the result. Rather than using double SHA-256, it uses Keccak-256 to generate four checksum bytes. These are added at the end of a string. Once the checksumbytes are converted to base58, you have the final address--and yes, it’s very long.
43ZZViHQKd42X7cajEtc6NUoxG4AvyMu3ZqpGTBP85uhEfYoPVAuGHxJcomMHEPp3NWiKJRUMnuAJ7dfBrPTcfjYMPJzz2a
Remember, don’t get caught up in the variety of addresses generated--they just serve as a means to accept a payment, which is assigned to a certain public key.
Thus, it doesn’t matter what you do with the public key, what cryptographic algorithm you apply to convert it to an address of sorts, and how it is formatted.
Ethereum’s Different
While Ethereum’s address is similar to Bitcoin’s, it differs in two ways:
- The length is much shorter, leaving a 32-byte string (rather than a 64-byte screen) and
- No checksum
Shorter Length
You start with a private key and use ECDSA to generate the 64-byte public key, which is hashed with Keccak-256. The result is the 32-byte string, where the first 12 bytes are dropped, leaving 20 bytes which comprise of a 40 character address. At that point, the prefix “0x” is added to the address. As Ethereum doesn’t convert the address to base58, it’s left in hexadecimal (0-F).
No Checksum
While any hexadecimal 40 character string can be an Ethereum address, the ethereum developers (like bitcoins) also heavily discourage users from manually typing in such a long address, risking any potential clerical or typographical error which could lead to a loss of funds.
What You Can Expect
Most Ethereum developers prefer the ICAP format, which like bitcoin addresses, also uses base58 characters and includes a checksum.
E7338O073KYGTWWZN0F2WZ0R8PX5ZPPZS
ICAP, to its advantage, is a fully valid International Bank Account Number (IBAN), which allows for existing bank software to understand interact with it. IBAN is the international identifier of client accounts in the banking industry, which consists of 32 case-insensitive alpanumeric characters, a country code, a checksum, bank number, and account number.
Ethereum’s Different
But you may find STEEM, a cryptocurrency based on the BitShares concept to be more user-friendly and time-friendly. Why?
Interlinked with the Steemit platform, STEEM has a similar system to that of Ethereum--your username in STEEM is also your wallet address.
The difference with STEEM, is the architecture behind the name addresses. For more information on this, please click here.
Back in February, TRON founder, Justin Sun acquired Steemit, creating a wave of drama throughout the industry. For more information on this, please click here.